Indian Customs EDI System
The Indian Customs EDI Systems (ICES), a flagship application of NIC, was launched in the year 1995. It is the outcome of a systems study conducted by National Informatics Centre and Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs in 1992 at number of Customs Houses throughout the country. The key element of the application is connecting all the players involved in international trade with the Customs House electronically.

The core functionality of the Indian Customs procedures has been fully automated through ICES. Large number of documents that trade, transport and regulatory agencies (collectively called Trading Partners) are required to submit/ receive in the process of live customs clearance are now being processed online. It is now operational at 260 (Approx) major customs locations and 300 (Approx) Special Economic Zone (SEZ) locations, handling nearly 99% of India’s International trade in terms of import and export consignments.
The main objectives set for the Indian Customs EDI System:
- Computerization of customs-related functions including import/export, general manifest control, ex-bond clearance of warehouse goods, goods imported against export promotion schemes, and monitoring of export promotion schemes.
- To exchange information with trading partners like ports, DGFT, airlines, shipping lines, shipping agents, banks, participating government agencies, DRI, DGCIS, DoV, and many more government and non-government agencies.
- To become vital pillars of the Indian Economy and to improve ease of doing business.
- Reduce interaction of the trade with Government agencies
- Guiding principles for ICES are facilitation, accountability, consistency, transparency and simplification
Customs Export Facilitation – NIC as Technology Partner
- New Modular Facilities
- Introduction of GST cess for clear accounting heads
- Facilitation of DGFT to release ROSL license
- Introduction of new module – Fail after success case bank credit of GST refund
- Facility to view foreign exchange realization to customs official
- Streamlining of alert modules by introduction of new role exp alert
- New module for road transshipment of cargo from air sites
- Number of facilitations to exporters during this tough time
- Increase validity of Export Document (SB) to 30 days – To handle slow movement of cargo
- Automatic release of withheld GST refund – To handle cash crunch
- Increase in number of documents in scroll from 2000-5000 – For fast payment of refunds
- Single window
- Email/SMS information to Exporter for their incentives/queries etc.
- Paradigm shift from document clearance to Cargo movement
- Implementation of messages
- E-seal (Exporter – Customs – Exporter)
- Custodian (Custodian – Customs – Custodian)
- Transhipper (Transhipper – Customs – Transhipper)
- CSN (Shipping line – Customs – Shipping line)
- Environment-friendly measurement
- e-LEO SB copy
- e-Gate pass challan
- Utilities for preparing e-docs for SCTMR – custodian, transhipper, shipping line etc.
- Online bank account registration

ICES has two aspects
- Internal Automation of the Custom House for a comprehensive, paperless, fully automated customs clearance system that makes the functioning of Customs clearance transparent and efficient.
- Online, real-time electronic interface with the trade, transport, banks, and regulatory agencies concerned with customs clearance of import and export cargo through ICEGATE.
To meet the objective of proving a more efficient, transparent, and standardized Customs assessment experience, “Faceless Customs” has been implemented. This revolutionary step has covered that extra mile in reducing Trade and Customs physical interaction as the document assessment process has gone truly national. The Exporters/Importers are transparent to the fact as to where the documents are being assessed.
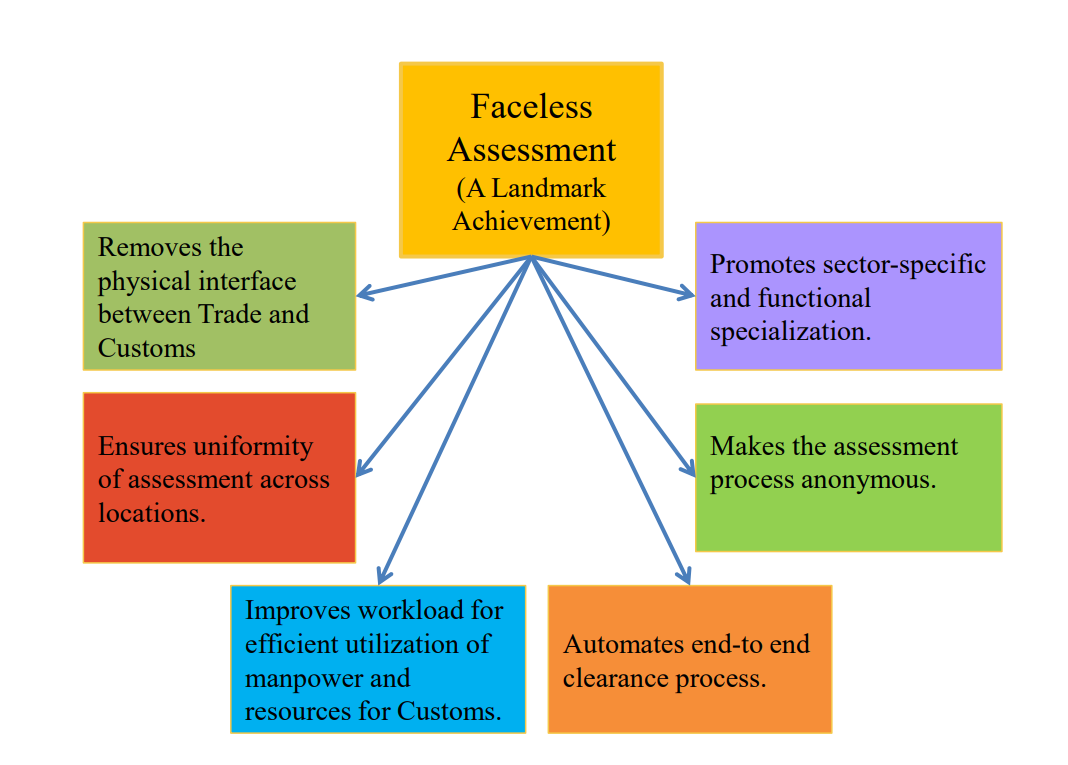
Faceless Assessment (A Landmark Achievement)
- Removes the physical interface between Trade and Customs
- Promotes sector- specific and functional specialization
- Ensures uniformity of assessment across locations
- Makes the assessment process anonymous
- Improves workload for efficient utilization of manpower and resources for Customs
- Automates end-to-end clearance process
Major Components of Indian Custom automation
- ICEGATE is the interface of ICES with the external world for customs clearance related messages and sharing of trade Statistics/Customs clearance data with licensing and regulatory agencies such as DGFT, DGCI&S, Ministry of Steel, RBI etc.
- ICES automatically receive and process all incoming messages. ICES generate all outgoing messages automatically at the appropriate stage of the clearance process.
- Single Window Interface for facilitating trade (SWIFT) – ICES allow importers and exporters, the facility to lodge their clearance documents online at a single point only. Required permissions, if any, from other regulatory agencies is obtained online without the trader having to approach these agencies. The Single Window Interface for Trade (SWIFT) has reduced interface with Governmental agencies, dwell time and the cost of doing business.
- E-Sanchit to facilitate trade paperless processing of documents has been introduced. The idea is to reduce physical interface between customs regulatory agencies and the trade and to increase the speed of clearance.
Remote EDI System (RES) is windows-based series of packages which facilitates the Custom House Agents/ Importers/ Exporters in preparation of Bill of Entry, Shipping Bill, Import Report, Export Report, Consol Manifest declarations in the format acceptable to ICES for remote submission at Customs House through Indian Customs EDI Gateway (ICEGATE). The Exporters, Importers and Custom House Agents (CHAs) can submit all related documents through the Remote EDI Software (RES), which is a standalone software package developed by NIC.
ICES: Major Components
- ICES Imports – The main features of ICES Imports module are the following:
- Online duty payment & GST Refund.
- Imports Declaration.
- Faceless, Paperless import document processing.
- Data exchange with government agencies.
- Union Budget implementation every year.
- ICES Exports – The main features of ICES Exports module are the following:
- Assessment and Let Export Order.
- Exports Declaration.
- Incentive Disbursement.
- Foreign Exchange.
- Tight Coupling with DGFT for licenses.
- Union Budget implementation every year.
- Remote EDI System (RES) – RES is windows based series of packages which facilitates the Custom House Agents / Importers / Exporters in preparation of Bill of Entry, Shipping Bill, Import Report, Export Report, Consol Manifest declarations in the format acceptable to ICES for remote submission at Customs House through Indian Customs EDI Gateway (ICEGATE). The Exporters, Importers and Custom House Agents (CHAs) can submit all related documents through the Remote EDI Software (RES), which is a standalone software package developed by NIC.
- ICETAB – A tablet application that enables customs officers to perform real-time, paperless examination and clearance tasks. With its user-friendly interface and seamless integration with other customs systems, ICETAB ensures quick and transparent uploading of examination reports.
- Special Economic Zone (SEZ) – A Special Economic Zone (SEZ) is a specifically designated area within a country that operates under different economic regulations than the rest of the nation, with the aim of attracting foreign investment, boosting exports, and promoting rapid economic growth. The online operations of SEZs are integrated into the Indian Customs EDI System (ICES) to streamline and automate customs processes. ICES provide real-time updates and comprehensive data management, enabling SEZ businesses to manage logistics efficiently and comply seamlessly with regulatory requirements.
- Cargo Manifest and Transhipment Regulations (SCMTR) – The Sea Cargo Manifest and Transhipment Regulations seek to bring about transparency, predictability of movement, and advance collection of information for expeditious clearance. The new regulation stipulates changes in timelines and requirements for advance notice by shipping lines (vessels) arriving in and going out of India.
- Foreign Post Office (FPO) Imports – The application is developed to digitize all postal imports and their electronic clearances, and it is integrated with ICES. The application integrates with India Post (DoP) systems through APIs and aims to digitize the entire process. This includes handling the receipt of Customs declarations as Electronic Advance Data (EAD), tracking arrival information from the Department of Post, and ensuring the delivery of goods to the recipient after completing all customs procedures.
- Advance Passenger Information System (APIS) – The Advance Passenger Information System (APIS) is a critical tool for enhancing border security and combating smuggling. It compiles the passenger details and flight information, from airlines for all international flights arriving and departing from India. These details are shared with Indian Customs and other security agencies to identify potential suspects by cross-matching data with watch lists, including Look Out Circulars (LOCs) and red corner notices. APIS has been instrumental in tracking smuggling activities involving gold, narcotics, illegal cash, and other contraband.
Trade Facilitation:
- Electronic Cash Ledger
- Single Window Interface for Trade (SWIFT) clearance.
- Electronic exchange of information.
- Data analytics for investigation agencies.
- ICETRAK mobile app to track Import/Export documents.
- e-LEO (Let Export Order)/OOC (Out of Charge) copy.
- e-Gate pass challan.
- Online bank account registration.
Performance Indicators:
- The ICES application handles approximately 99% of India’s international trade.
- It is operational at around 560 locations across the country.
- Approximately 55 lakh Bills of Entry (BEs) are filed annually.
- Approximately 92 lakh Shipping Bills (SBs) are filed annually.
- Total customs duty collected annually is around ₹7,65,660 crore.
- Total incentives paid annually amounts to approximately ₹26,760 crore.
Performance Indicators:
- Minimize personal interaction of Trade with Customs officers and various Government agencies like DGFT, EPCs, Ports, Airport Authority of India, and Banks. This has been achieved with a robust message exchange mechanism among various stakeholders
- Consolidation of Data for National Level MIS.
- Accuracy, transparency, accountability, and better supervision.
- Standardized procedures across the country.
- Reduced cost of processing documents.
- Electronic clearances provided quicker cargo releases, resulting in reduced dwell time.
- Improved Security and Risk Management.
- Centralized Directory Management.
- Centralized License and Bond Management.
- Harmonized business relationships with Customs Community members, namely Ports, DGFT, Airlines, Container Depots, etc.
- Electronic messaging resulting in minimized data capture.
- Secure data sharing between different agencies.
For details, please visit: https://ices.nic.in/
